On one particular occasion, Calvin Coolidge was invited to dedicate the cornerstone of a local building. Presented with the ceremonial spade by the emcee, the President dutifully performed the honors and prepared to leave. Gently reminded that it was customary to say a few words, he paused to look at the clod of dirt he had just overturned as if something very profound was on his mind for this occasion. Gazing intently at the ground for a moment, he noticed a plump nightcrawler emerging from the freshly disturbed earth. Without a hint of a smile, he uttered the droll phrase above and went on his way. If there was any laughter by those who got the joke, he never waited to be appreciated for the punchline. Cal was already on to the next task. Such was the dry and homespun humor of our thirtieth president.
honesty
“James Madison vs. Barack Obama” by Burt Folsom
“James Madison vs. Barack Obama” by Burt Folsom
Taking a series of powerful reminders from the Progressive Era (1900-1920), Dr. Folsom reveals the inescapable flaws of trusting government bureaucracy with competence and responsibility for human life and the daily decisions we, as free individuals, are infinitely better equipped to make. It is the stark difference between the blind reliance on government “experts” and the wisdom of the Constitution in liberating people to choose for themselves rather than live at the behest of an unbounded bureaucracy. It is the naive notion of progressives then as now that tighter controls make happier people and better nations while constitutionalists, who understand what power does to human nature, embrace a limited government, where power is disbursed and held strictly accountable to the people. Constitutionalists grasp the inhumane character of bureaucracy because history has taught them political calculations take primacy over the liberty of people and an equal respect for the law. To constitutionalists, limiting what government can do, preserving equality under the law and retaining each person’s freedom to pursue happiness comprise the compassionate way. It is the recipe by which America has experienced so many blessings and so much success. Despite the best efforts of progressives, no bureaucratic system will ever come close to the tremendous success of constitutionalism, when it is practiced.
Our thirtieth president, living in the midst of the Progressive Era, understood this well. He would come down decisively on the side of rolling back the growth and expansion of government, looking to the ingenuity and ability of the people to govern themselves. His appraisal of real progress grounded in the sensible and prescient foundations of constitutionalism make Coolidge not only a rewarding subject to study but a necessary one today. No need to take my word for it, Coolidge encapsulates it best:
“When we contemplate the enormous power, autocratic and uncontrolled, which would have been created by joining the authority of government with the influence of business, we can better appreciate the wisdom of the fathers in their wise dispensation which made Washington the political center of the country and left New York to develop into its business center. They wrought mightily for freedom…When government comes unduly under the influence of business, the tendency is to develop an administration which closes the door of opportunity; becomes narrow and selfish in its outlook, and results in an oligarchy. When government enters the field of business with its great resources, it has a tendency to extravagance and inefficiency, but, having the power to crush all competitors, likewise closes the door of opportunity and results in monopoly” – November 19, 1925.
“No plan of centralization has ever been adopted which did not result in bureaucracy, tyranny, inflexibility, reaction, and decline. Of all forms of government, those administered by bureaus are about the least satisfactory to an enlightened and progressive people. Being irresponsible they become autocratic, and being autocratic they resist all development. Unless bureaucracy is constantly resisted it breaks down representative government and overwhelms democracy. It is the one element in our institutions that sets up the pretense of having authority over everybody and being responsible to nobody” – May 15, 1926.
“The government has never shown much aptitude for real business. The Congress will not permit it to be conducted by a competent executive, but constantly intervenes. The most free, progressive and satisfactory method ever devised for the equitable distribution of property is to permit the people to care for themselves by conducting their own business. They have more wisdom than any government” – January 5, 1931.
“Neither the state nor the Federal governments can supply the information and wisdom necessary to direct the business activity of the nation…The experience, skill and wisdom necessary to guide business cannot be elected or appointed. It has to grow up naturally from the people. The process is long and fraught with human sacrifice, but it is the only one that can work” – May 1, 1931.
In contrast to the destruction of society by bureaucracy, “There is another system with which every American should be familiar, a system of equality and of freedom, not without the claim of divine right but recognizing that such right reposes in the people; a system where the individual is clothed with inalienable rights, the people are supreme, the government is their agent. Under this conception there is real freedom, real independence, and grave personal responsibility. The rulers look to the people. Their authority is the public will, ascertained in accordance with law. There will be the least possible interference with private affairs. Realizing that it is the people who support the government and not the government which supports the people, there will be no resort to paternalism. Under such institutions there may be appear to be a lack of machine-like efficiency, but there will be no lack of character. Private initiative will be stimulated. Self-reliance and self-control will be increased. Society will remain a living organism sustaining hope and progress, content to extend its dominion not by conquest but by service. Such is the system of self-government, the orderly rule of the people, carrying within itself a remedy for its own disorders and the power of self-perpetuation. This is the ideal of America” – January 21, 1923.
Coolidge, one of our wisest constitutionalist Presidents, hits the mark, as usual, squarely and faithfully.
On the Business Organization of the Government
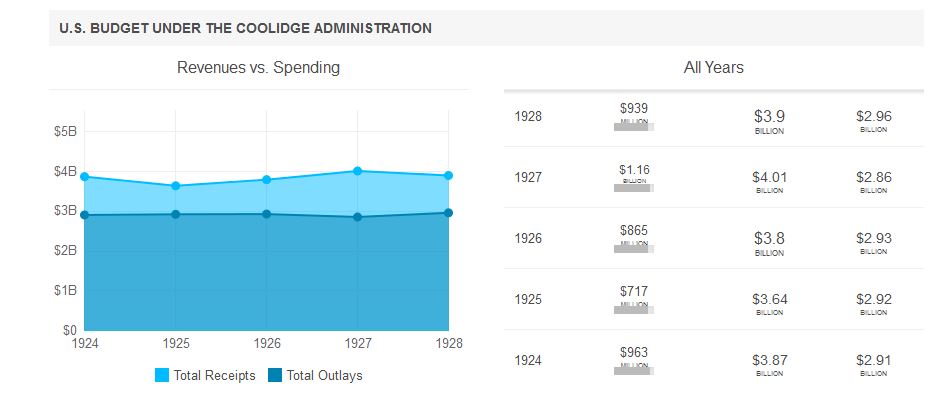
While this source parrots much the same accepted narrative for Coolidge’s supposed “do nothing” time in the White House, these numbers comprise part of a sizable record contradicting that biased claim, shattering much of the shallow veneer plastered up against the Coolidge Era for far too long by New Deal “historians” like Art Schlesinger, William Leuchtenburg and those who echo their assumptions. http://us-presidents.findthebest.com/l/12/Calvin-Coolidge.
This month, like January, held a special place during the Coolidge years. It was the continuance of a tradition begun under Harding but abruptly ended with his successor, Hoover. It would come to carry the resolute Vermonter’s unique imprint on its importance to transparent and sound government. It was the bi-annual meeting for the Business Organization of the Government. Held for eight years in various auditoriums around Washington, from the Interior Department offices to the Continental Hall, Coolidge would take part in no less than ten such gatherings.
The Budget and Accounting Act of 1921, shepherded to passage by Harding and its first Director, General Charles G. Dawes, brought what had been an arbitrary and chaotic budget process to order. Some years would see more than twelve competing budgetary packages presented to the Congress from the various bureaus, departments and agencies in Washington. Requests would often be made for the same appropriated amounts, with Congress left to sort out and streamline the tangled mess. The Budget Act changed all of that, restoring authority for Executive Branch responsibilities to the President. Now it was through the Chief Executive that all Cabinet heads and bureau chiefs had to request their respective budgeted funds, not the Congress. It served to reaffirm the Constitution’s separation of powers but also to put the brakes on a random exchange of favors and hold the Federal Government to the discipline of time-tested household budgeting. Harding and Director Dawes would lead the first meeting on June 29, 1921. As Harding’s momentum slowed, it would fall to Coolidge, even as Vice President, to present the case for what would come to be called “scientific economy.” It would be the preparation of Calvin Coolidge that particularly qualified him more than any of his contemporaries in the White House to exercise the necessary perseverance to follow-through with a consistent restraint of Congressional spending on one side and Executive regulation on the other.
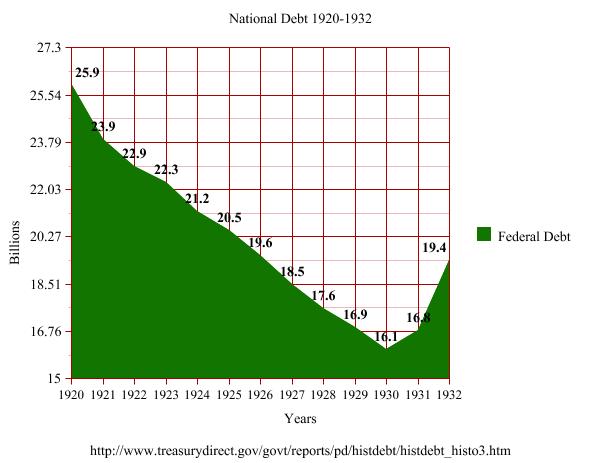
Graph encompasses the final year of President Wilson through the third year of President Hoover. Notice the consistent retirement of debt each year of the Harding and Coolidge administrations. It was so strong a system that it carried forward into Hoover’s first year, until spending resumed its climb from 1930 onward.
Unlike many of his peers however, his accomplishments did not end with rhetoric. He practiced what he preached, holding firm grasp on the White House staff budget, a duty he viewed as under his own personal purview. He left office having saved most of his $75,000 annual paycheck. He achieved what so many, even the great Ronald Reagan, failed to do: actually reduce Federal spending while paying down the nation’s debt from $25.9 to $16.9 billion in six years. He did so not by “wheeling and dealing” with the very recalcitrant Republican Congress of his day, but by winning their respect with his honesty, political experience and courage. He did not flinch when lesser men did. While he left many wondering at how he was able to co-opt allies and neutralize opponents, he never exchanged what was right for everyone in place of personal electoral advantage. In this way he proved successful in anticipating what Congress would see and do, as Dawes later noted of him, better than the House and Senate themselves most of the time. Yet, Hoover, in part because of his refusal to recognize Congress’ role as legitimate, would see his work frustrated and his goals repeatedly redirected. On the other hand, it was Coolidge’s fairness, good sense and integrity that equipped him to overcome each challenge and keep the agenda moving.
Coolidge made it plain in his Autobiography that he refused to take reprisals or exert coercion on those who disagreed with him (p.232). He simply exercised his responsibilities justly and impartially, keeping his door open to everyone. If they passed disagreeable legislation, he had the veto, which was used fifty times during his tenure. He hardly operated alone, appointing able men like C. Bascom Slemp and Everett Sanders, former Congressmen, who knew the political topography like few did. He also had the determined General Lord, whom he consistently backed with each decision to cut, eliminate and chip away at Washington’s wasteful expenditures. When the issue, no less contentious than now, concerned budgeting and taxes, he was particularly apt at taking his reasons directly to the American people on these two grand occasions each January and June, letting them see and especially hear the logic behind and importance of “scientific economy.”
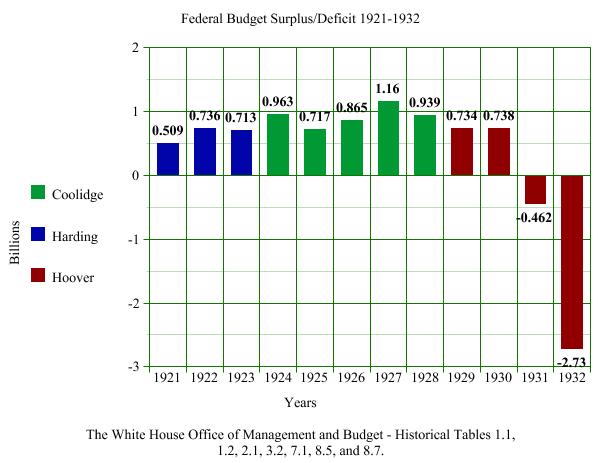
A look at the Federal Budget Surpluses and Deficit totals from Harding through Hoover after the Budget and Accounting Act of 1921. Coolidge maintained healthy surpluses all six years of his tenure. It was Hoover who ended that achievement and suspended the bi-annual meeting of the Business Organization of the Government.
In the coming weeks, we will showcase some of the highlights of the ten speeches he made before the Business Organization of the Government as President, most of which were carried over the radio for millions of Americans to listen in for the first time. Marshaling his talent for this new medium combined with a very genuine passion for strict economy, Coolidge even infused a strong sense of dramatic flare to make his case directly to us. In this impressive fusion of salesmanship and substance, it marked an incredible time in American history when none less than the President of the United States championed good governance and constructive economy.


